Strategic Brand & Intangible Valuation
Strategic Brand & Intangible Valuation
Introduction to Strategic Brand and Intangible Valuation Introduction
The importance of Brand and intangible valuation in the modern economy based on knowledge and reputation has become an essential element of corporate, financial reporting, and investment decision-making. Since the proportion of tangible assets in the enterprise value is steadily decreasing, it is brands, intellectual property, customer relationships, and proprietary technologies that become the key motivators of sustainable growth in organizations.
Meanwhile the increases in expectations with regard to transparency, standardization and investor protection have further focused attention on the issues of valuation practices. Approachable, acceptable, and defendable methods of valuing intangible value are offered by established models, including brand finance intangible assets methodologies, which are consistent with aicpa intangible asset valuation principles. These frameworks promote financial reporting, as well as strategic planning, mergers and acquiring, licensing, taxation and dispute resolution.
This paper will explore the fundamental tenets of the brand and intangible valuation, major standards of professional practice, and the organizations can consider the valuation practice as the part of the long-term value generation and governance.

Brand and Intangible Valuation, Strategic
The principle of brand and intangible valuation has been rooted in the notion that most of the contemporary most valuable corporate assets are either not tangible. Brands affect the preference of customers, pricing power, and loyalty whereas patents, software, data, and proprietary processes produce barriers to entry and competitive advantage over time.
Financially, the gap between market capitalization and book value is to a greater extent due to intangible assets. The intangible assets unlike the physical ones, which are easily noted by the conventional accounting systems, need the assistance of skilled study which would combine the financial, marketing, legal and strategic factors. This has consequently made brand and intangible valuation a multidisciplinary practice and not an accounting practice.
Companies that can recognize, quantify, and account the intangible value are in a better position to explain themselves better to investors, regulators and strategic partners.
Brand and Intangible Valuation Strategic Importance
On top of regulatory compliance, the brand and intangible valuation is a strategic factor in corporate decision-making. The results of valuation have an effect on capital allocation, brand architecture, pricing strategy, and optimizing portfolios. In measuring the economic value of intangible assets, executives are able to justify long-term investment that is unlikely to translate into short-term financial benefits.
During mergers and acquisitions, intangible valuation plays a key role in purchasing price allocation as well as integration after the transaction. Proper valuation helps the acquirers to establish significant drivers of value and come up with strategies to either maintain or improve them. Likewise, intangible valuation and brand is the basis of royalty creation, licensing and franchise deals.
As competition mounts pressure, and stakeholder comprehensiveness rises, the capacity to support intangible worth through accepted approaches has become one of the indicators of good corporate governance.
Introduction to Brand Finance Intangible Assets Methodologies
The framework is defined as structured approaches which are meant to categorize, quantify and report intangible value in a clear and comparative way. Such methodologies differentiate between identifiable and non-identifiable intangible assets that include trademarks and patents, respectively, and goodwill.
In this context, the brands are considered as detachable economic resources that could lead to an economic pay-off in the future. The usual methods of valuation involve the income approach, market approach and cost approach and brand specific models usually focus on the income based methods which are associated with brand based earnings.
Another key characteristic of brand finance intangible assets approach is that it is benchmarking, comparability which allows organizations to evaluate brand performance in relation to competitors and track changes over time.
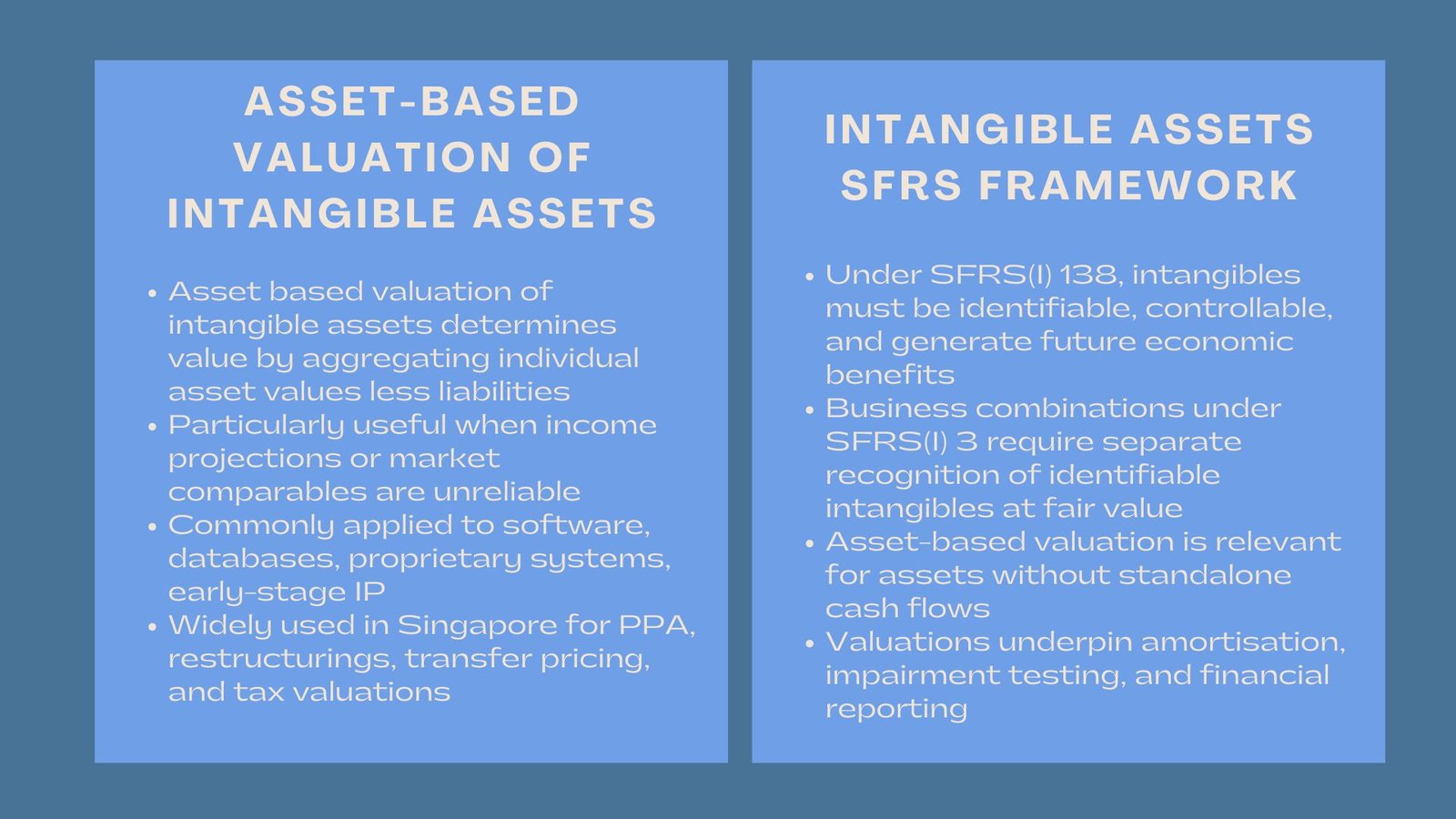
Intangible Assets
This refers to assets like brand name, goodwill, and trademarks that are not tangible; these do not possess monetary value. Connection of Intangible Assets with Financial Performance: Intangible Assets are those assets that are not tangible such as the brand name, goodwill, and trademarks, which have no monetary value.
A major issue of brand and intangible valuation is determining an explicit and justifiable relationship or linkage between intangibles and financial performance. Brands generate revenue by leading to customer preference and less price elasticity as well as by enhancing market expansion and other intangibles operate by creating cost efficiencies and risk reduction.
High-quality valuation models separate incremental cash flows of particular intangible assets, backed by sound information, clear assumptions and well-defined value drivers. Brand strength indices and risk-adjusted discount rates are frequently included in the brand finance intangible assets methodology as a measure of the sustainability of brand-related earnings.
This will provide the opportunity to assess the intangible assets on the basis of their economic contribution to the company, as opposed to abstract brand performance.
AICPA and the Professional Standards
The professional standards are essential in determining consistency, objectivity, and credibility in the valuation practices. The aicpa intangible asset valuation framework offers a guideline that is principled based and can be used in the context of financial reporting, litigation, and taxation.
Consistent with other broader valuation standards, aicpa intangible asset valuation focuses on identifying the clear asset, stated purpose of valuation, reasonable standards of value and clearly documented assumptions. Valuers should use strict procedures that capture the view of the market players.
In case of organizations with regulative settings or which are liable to audit review, the principles of aicpa intangible assets valuation raise defensibilities and mitigate the chances of controversy or recalculations of finances.
The combination of Valuation and Financial Reporting
Althrough brand & intangible valuation goes beyond accounting, it is important to incorporate it with financial reporting. Accounting standards only list intangible assets as a component of business combinations, impairment testing, and limited cases concerning internally generated assets.
Such frameworks as brand finance intangible assets facilitate this integration through the alignment of strategic valuation information and reporting requirements. When these are used together with aicpa guidance on intangible assets valuation, organizations are capable of generating valuation reports that will be acceptable to the internal decision-makers, auditors and external stakeholders.
Such integration increases transparency and builds investor confidence.
Valuation Strategies and Methodological issues
The choice of the right valuation method is the key to successful brand and intangible valuation. Commonly used methods include income based techniques in which brands and customer related assets would be used, market based techniques which are based on similar transactions and cost based techniques which estimate replacement or reproduction costs.
Both strategies possess their own strengths and weaknesses and need professionalism and background knowledge. Brand finance intangible assets framework combines quantitative analysis approach with qualitative evaluation to measure brand-specific risks and opportunities.
According to aicpa principles of intangible asset valuation, the methodological decisions should be consistent with the purpose of valuation and properties of the assets with clear assumptions and records.
Compliance, Governance and Risk Management
Good brand and intangible valuation promotes risk management and corporate governance. Companies should be careful about exaggerated or insufficiently supported valuations that may attract regulatory attention, lawsuits by investors and reputational risk, when undervalued; and inadequate strategic decisions can be made.
Brand finance intangible assets approaches to governance structures allow the systematic oversight of the intangible value by conducting regular valuation reviews, sensitivity analysis and impairment testing. Adherence of compliance to aicpa intangible asset valuation helps to enhance governance by providing clarity, consistency and accountability.
Non-Financial and Strategic Applications
In addition to financial reporting, brand and intangible valuation also inform strategic actions like investment in brands priority, rationalization of the portfolio and entry decisions. Joint ventures, licensing and strategic alliances negotiations are also negotiable through valuation insights.
The brand finance intangible assets perspective enables organizations to compare the performance of the brand and where it can improve on it. These insights, together with aicpa intangible asset rigour of valuation, can be put to action and be defended at the executive level.
Next Generation Brand and Intangible Valuation
Future brand and intangible valuation opportunities will be determined by the development of data analytics, the emphasis on sustainability, and the new expectations of the stakeholders. The brand perception and value in the long run are becoming more subject to environmental, social and governance factors, which necessitate a change in the valuation models.
Although technological advancement improves the availability of data and sophistication of the models, professional judgment is a necessary element. The component by component credible-valuation frameworks like brand finance intangible assets and aicpa intangible asset valuation will continue to offer credible valuation frameworks in the ever-increasingly complex business environment.
Conclusion
Brand and intangible valuation has taken its place as an element of strategy, governance and financial reporting in an economy where intangible assets prevail. The use of systematic methodologies which fits the brand finance intangible assets models and the aicpa intangible asset valuation models can produce credible, transparent and actionable results of valuations.
Valuation when inculcated in decision-making processes, improves the process of capital allocation, investor confidence, and sustainable value creation. With markets ever-changing, it is still the capacity to explicitly define and manage intangible value that will make successful organizations characteristic.